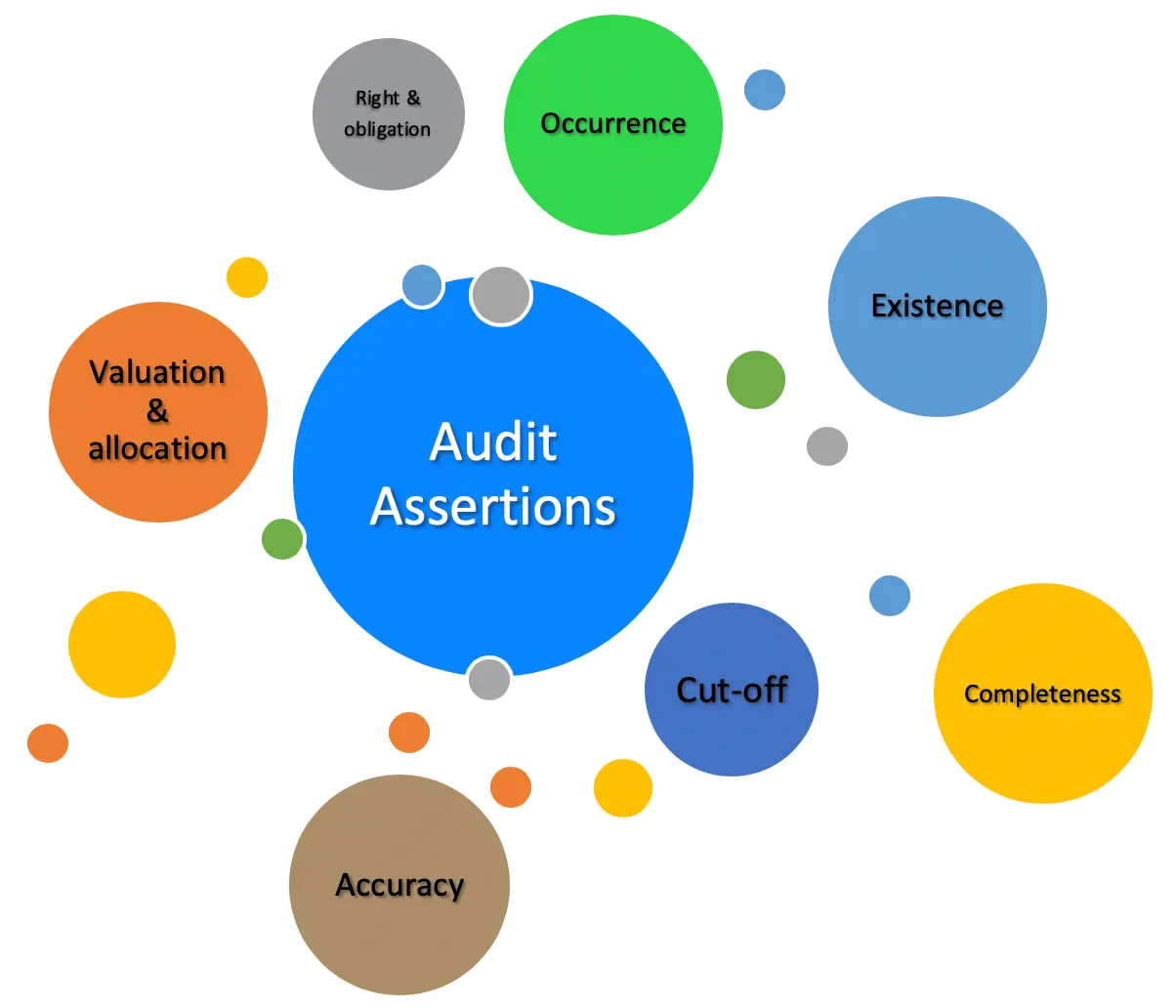
Auditors consider financial statements assertions to identify appropriate audit procedures. What are Financial Statement Assertions. The existence assertion is that any assets and liabilities recorded in the financial statements actually exist. Typically those that own a company the shareholders are not those that manage it. Financial and other information are dis-. Assertions for Classes of transactions statement of profit loss Assertions for account balances. Auditors consider financial statement assertions to identify appropriate audit procedures. The assertions form a theoretical basis from which external auditors develop a set of audit procedures. Purpose of a financial statement audit Companies produce financial statements that provide information about their financial position and performance. For items a through f match each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning.
Assertions for Classes of transactions statement of profit loss Assertions for account balances. Purpose of a financial statement audit Companies produce financial statements that provide information about their financial position and performance. Audit Assertions are also known as Management Assertions and Financial Statement Assertions. For items athrough fmatch each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning. This information is used by a wide range of stakeholders eg investors in making economic decisions. For items a-f match each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning. These assertions are noted below. Auditors consider financial statement assertions to identify appropriate audit procedures. For example ordinarily more evidence is needed to respond to significant risks. Also known as management assertions or financial statement assertions audit assertions are the claims made by management certifying the financial statements presented are complete and accurate.
Also known as management assertions or financial statement assertions audit assertions are the claims made by management certifying the financial statements presented are complete and accurate. For items a through I match each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning Each statement may be used only once HET All assets have been recorded. Each statement may be used only once. These assertions are noted below. Existence and occurrence d. Earlier application is permitted. Assertions Transactions include sales purchases and wages paid during the accounting period. The existence assertion is that any assets and liabilities recorded in the financial statements actually exist. Auditors consider financial statement assertions to identify appropriate audit procedures. Each statement may be used only once.
The auditor should consider the sufficiency and appropriateness of audit evidence. Financial statement assertions are claims made by an organizations management regarding its financial statements. 8 rows Audit assertions financial statement assertions or managements assertions are the claims made by the management of the company on financial statements. Auditors consider financial statements assertions to identify appropriate audit procedures. The existence assertion is that any assets and liabilities recorded in the financial statements actually exist. Assertions for Classes of transactions statement of profit loss Assertions for account balances. Auditors consider financial statement assertions to identify appropriate audit procedures. When a companys financial statements are audited the principal element an auditor reviews is the reliability of the financial statement assertions. They may be explicit ie stated directly or. As the risk increases the amount of evidence that the auditor should obtain also increases.
For liabilities auditors need to. For items a through f match each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning. For assets it usually comprises testing the physical existence. The assertions form a theoretical basis from which external auditors develop a set of audit procedures. Similarly it includes a claim that there is no overstatement in reporting these items. For items a through f match each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning. As the risk increases the amount of evidence that the auditor should obtain also increases. Existence and occurrence d. Purpose of a financial statement audit Companies produce financial statements that provide information about their financial position and performance. For items a through I match each assertion with the statement that most closely approximates its meaning Each statement may be used only once HET All assets have been recorded.